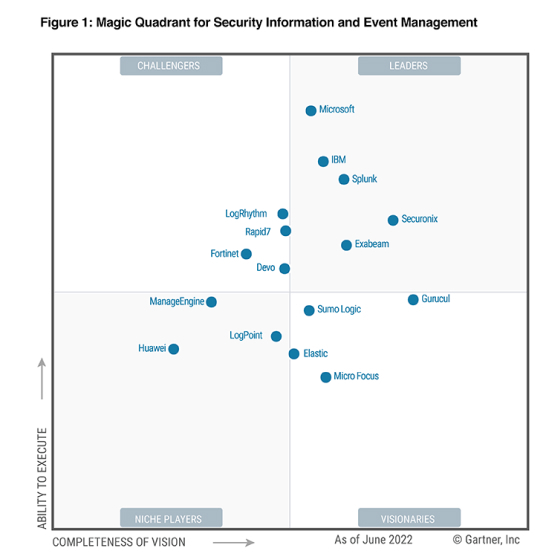
Get the report
MoreSOAR stands for security orchestration, automation and response. Coined by Gartner in 2017, SOAR describes the potential merging of three distinct and interconnected markets:
Security orchestration and automation (SAO)
Threat intelligence platforms (TIP)
Security incident response platform (SIRP)
Fused, these three markets create the technology known as SOAR, which leverages machine learning and progressive automation to accelerate incident response time and improve overall SecOps efficiency.
SOAR was created to overcome common obstacles that torment obsolete technologies in a SOC. SOAR is meant to act as a force multiplier, a connective tissue that enhances the productivity of every other tool and technology it collaborates with within the SOC.
SOAR works on optimizing processes and allows the orchestration of many different technologies into standardized response procedures for each type of attack, called Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). It also automates all the repetitive tasks within these processes and ensures that all analysts follow the same procedures.
What is a SOAR platform?
A SOAR platform is a tool that helps cyber security teams minimize response time, reduce analyst fatigue via orchestration and automation, and improve the efficiency and consistency of SOC processes. SOAR permits making the most of automation, orchestrating several tools with SOPs, creating immediate and detailed incident reports, and automatically assigning analysts only those tasks and decisions where human value is essential.
The difference between SIEM and SOAR
While SIEM detects potential security threats, SOAR takes alerts to the next level by beginning to triage and then applying processes to remediation, automatically assigning high-value tasks to analysts. SOAR extends beyond the use cases of SIEM by offering recommended means of response thanks to its machine learning prowess. SIEM is better at managing vast influxes of data from multiple sources. SOAR can’t replicate the value offered by SIEM and vice versa. Both solutions work best in tandem.
SOAR doesn’t replace SIEM but rather starts where SIEM ends. Both technologies have different strengths, and neither can replicate the value these technologies provide individually. SIEM excels at aggregating large quantities of data, while SOAR is unmatched in improving the productivity of SOCs via machine learning and automation.
Most importantly, SOAR and SIEM complement one another, which is why many SOCs rely on both technologies simultaneously.
Neither SIEM nor SOAR disrupts the natural workflow of the SOC they are deployed in. Their processes don’t contradict one another, and many organizations rely on both SIEM and SOAR. SIEM solutions usually produce more alerts than SOC teams can manage, and SOAR’s ability to handle all alerts quickly allows security teams to use both SIEM’s and SOAR’s strengths to the fullest.
SOAR’s strengths lie in its ability to learn repeatable patterns and behaviors and use the knowledge of historically accumulated data to accurately detect false positives. This helps analysts cope with the influx of alerts and focus on the threats that matter. To do this, SOAR uses machine learning to predict potential threat patterns and relies on automation to take care of manual operations.
SOAR’s singular goal is to help SOC teams become more efficient at detecting and nullifying incoming threats and speed up the time necessary to respond to and manage incidents.
The three core capabilities of SOAR are:
Orchestration: Through the orchestration of technology, processes, and people, SOAR enables security teams to work as a unified entity to ensure that security programs operate in an optimized manner. By orchestrating various technologies, SOAR helps security professionals correlate and easily access information from disparate systems, ultimately allowing them to establish repeatable incident workflow responses and make faster and well-informed decisions.
Automation: SOAR automates the most basic forms of threat analysis, thus eliminating the need for SecOps teams to go through manual checks and freeing up their time for threats that require their attention. SOAR can also be instructed to automate complex and high-risk operations as well. Driven by machine learning, SOAR uses progressive automation to learn repeatable patterns, distinguish between real threats and false threats, and offer recommended courses of action based on historical data via playbooks.
Measurement: SOAR supports multiple methods for displaying and visualizing relevant information in an easily comprehensible manner, helping security teams make informed tactical and strategic security decisions. By aggregating intelligence from a wide array of sources and presenting them in visual, custom-built dashboards, SOAR helps organizations elevate their level of coordination and measure the performance of security operations in an intuitive manner.
SOAR differs from other technologies in that it leans on machine learning to learn and predict repeatable patterns to help SOC teams intercept and approach cyber attacks in a preemptive rather than a reactive manner. SOAR аutomates manual labor, learns repeatable pattern behavior and tells apart false positives from false negatives. Thus, allowing security professionals to direct their time and effort on more important initiatives.
Other benefits include:
Minimize response time with automation, orchestration and insightful decision-making
Automate repeated response workflow
Speed up incident response and management time
Free up time for higher-priority tasks
Improve the alert triage process and detect false positives
Deal with the increasing volumes of alerts
Easily integrate with other tools and technologies
Increase overall cyber security ROI
Automate and customize KPI reports
Enhance threat intelligence
SOAR leverages the power of playbooks, machine learning, and progressive automation to enhance threat intelligence and speed up security processes.
Playbooks: A playbook can be defined as the sum of required steps and actions necessary to successfully respond to specific incidents and threats. Playbooks in SOAR are categorized as formalized and predetermined incident response workflows that ensure the required steps are implemented to comply with NIST or GDPR and lead to the most efficient outcome of incident management. Playbooks help analysts automate manual processes and consist of workflows and standard operating procedures that automate the operationalization of threat management from detection, triage, and investigation to containment.
Machine learning: The machine learning capability helps SOAR analyze the patterns of incoming threats and use that knowledge to prevent similar attacks in the future. SOAR recommends data-driven actions that predict the most desirable outcomes via machine learning. SOAR leverages rich and contextual data and uses machine learning to deploy effective strategies.
Progressive automation: Progressive automation leverages machine learning to sharpen its detection capabilities and carry out tasks to full completion without human supervision. This type of automation is called progressive because it is programmed to accumulate knowledge from the characteristics of different types of threats it encounters, and use that knowledge whenever an alert with a familiar pattern occurs. The level of automation is adjustable, and analysts can choose in which stage of the automation sequence they want to intervene.
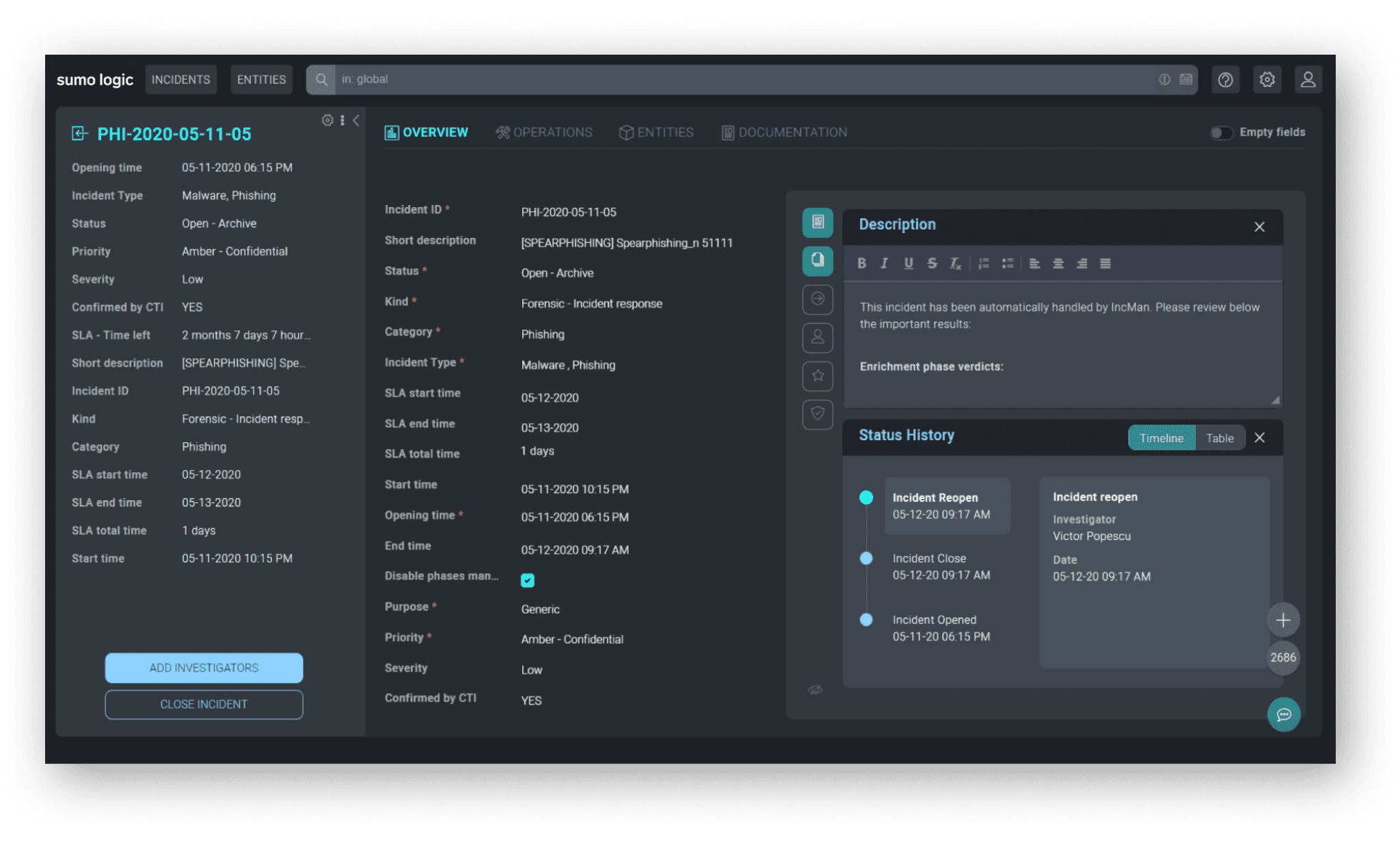
Sumo Logic can improve the efficiency of cybersecurity teams. Sumo Logic Cloud SIEM and Sumo Logic Cloud SOAR streamline the threat detection, investigation, and response process. Learn more about how Sumo Logic Cloud SOAR improves alert triage, analysis and investigation, incident assignment, playbook activation, standard operating procedure task management, and report creation.
Reduce downtime and move from reactive to proactive monitoring.